| source |
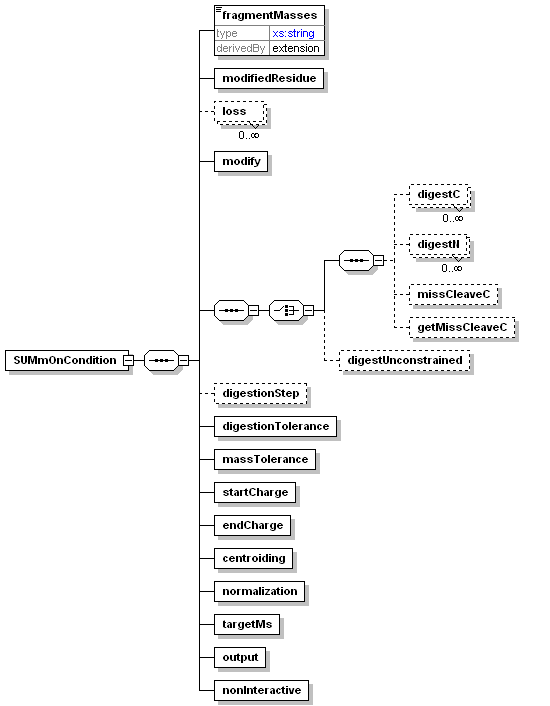
<xs:element name="SUMmOnCondition">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>This is the root element of a SUMmOn condition file.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="fragmentMasses">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The list of masses for the elemental units (e.g. amino acids in the case of a peptide) comprising the PTM under investigation. When using amino acid masses you should be carefull in setting the mass of the N/C terminal residues (i.e. remember to add one extra H or OH). Use a new line for every mass and a 0 to indicate the site of attachement to the target peptide.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="xs:string">
<xs:attribute name="type" type="xs:string" fixed="S">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>For the moment this attribute must be set to "S".</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="modifiedResidue">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Information on the site of attachment of the PTM.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="residue" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Amino Acid residue from the target peptide to which the PTM is attached to.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="notTerminal" type="xs:boolean">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Can the modified amino acid be at the termini of the target peptide. For instance attachment of SUMO to a Lysine residue hinders tryptic cleavage at that residue.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="loss" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A global loss that is applied to every fragment in the target peptide ion series (e.g. loss of water or ammonia).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="value" type="xs:double">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Mass in Da of the global loss.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="modify">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Modification to be applied to a specific amino acid from the target peptide.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="residue" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Modified residue.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="mass" type="xs:double">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Mass of the modification in Da.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="static" type="xs:boolean">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>1=static, 0=variable</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="digestC" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Digestion C terminal of a residue.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="residue" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The residue after which the digestion takes place.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="notResidue" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>If this residue is C terminal of the "residue" the enzyme will not cleave (use X if you always want a cleavage).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="digestN" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Digestion N terminal of a residue.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="residue" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The residue before which digestion takes place.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="notResidue" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>If this residue is N terminal of the "residue" the enzyme will not cleave (use X if you always want a cleavage).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="missCleaveC" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Adds up to "value" missed cleavages after "residue".</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="residue" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="value" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="getMissCleaveC" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Discards every target peptide that doesn't have exactly "value" missed cleavages at "residue". If residue is followed by "notResidue" it is counted both as a missed cleavage as well as a non missed cleavage.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="residue" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="notResidue" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="value" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="digestUnconstrained" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Digest unconstrained.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="residue" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Only keep residues that contain this residue.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="value" type="xs:int">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Maximal lenght of a target peptide.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="digestionStep" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Maximal number of proteins that will be digested at once when looking up the target peptides. This is only helpfull if you are using a big subDB.fasta and are running out of memory.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="value" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="digestionTolerance">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Tolerance (in Da) to be used when matching target peptide precursor ions.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="value" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="massTolerance">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Tolerance (in Da) to be used when matching fragment ions.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="value" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="startCharge">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The lower charge limit that SUMmOn will use when searching data for which the charge states have not been determined. The default value is 1.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="value" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="endCharge">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The upper charge limit that SUMmOn will use when searching data for which the charge states have not been determined. The maximal value is 9.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="value" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="centroiding">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>If your mzXML file contains profile mode data you must use this element to specify how to centroid it.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="type" type="xs:int">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>0=No centroiding, 1=Mathematical Averaging, 2=Weighted Averaging</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="iterations" type="xs:int" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The number of times the centroiding algorithm will run through the data (e.g. 4 should be a reasonable number).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="normalization">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>This for the moment should always set to "-2".</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="type" type="xs:int" default="-2"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="targetMs">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The MS level SUMmOn will analyze (e.g. 2 -> MS/MS ; 3 -> MS/MS/MS).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="level" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="output">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>1 will allow for more detailed post-analysis interpretation, but create a bigger file than 0.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="type" type="xs:int" default="1"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="nonInteractive">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>When set to 1 SUMmOn will save the results without switching to interactive mode in the middle of the analysis.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="value" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="description" type="xs:string">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Description of the content of condition file.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element> |